underlying profit что такое
underlying profit
1 underlying annual profit
2 underlying net profit
См. также в других словарях:
Underlying Profit — A term used to describe the actual reflection of a company s profit. The underlying profit is not the required accounting profit that is recorded on financial statements and documents mandatory to follow preset rules and regulations. This number… … Investment dictionary
Profit Range — A range of prices that an underlying security can possess in order for an investment strategy to be profitable. For some strategies, the position taken will have two break even points. The range between these two points serves as the… … Investment dictionary
Profit (accounting) — Accountancy Key concepts Accountant · Accounting period · Bookkeeping · Cash and accrual basis · Cash flow management · Chart of accounts … Wikipedia
Profit Motive — The intent to achieve monetary gain in a transaction or material endeavor. Profit motive can also be construed as the underlying reason why a taxpayer or company participates in business activities of any kind. Profit motive must be determined… … Investment dictionary
Tendency of the rate of profit to fall — The tendency of the rate of profit to fall (TRPF) is a hypothesis in economics and political economy, most famously expounded by Karl Marx in chapter 13 of Das Kapital Vol. 3. It was generally accepted in the 19th century. Economists as diverse… … Wikipedia
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis — Cost Volume profit (CVP), in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short run decisions. Cost volume profit (CVP) analysis expands the use of information provided by… … Wikipedia
paper profit — *Income (definition 2) that is not mirrored in underlying *cash flow. See also *unrealized gain … Auditor’s dictionary
Rio Tinto Group — Rio Tinto Limited plc Type Public company (ASX: RIO, LSE: … Wikipedia
The Co-operative Group — Co operative Group Ltd. Type Consumer cooperative Founded 1863 (1863) Headquarters … Wikipedia
Yorkshire Bank — Infobox Company company name = Yorkshire Bank company company type = Trading name/Subsidiary foundation = 1859 location=Leeds, England, UK key people = industry = Finance and Insurance products = Financial Services revenue = operating income =… … Wikipedia
Taxation in Germany — Taxes in Germany being a Federal Republic are levied by the federation ( Bund ), the States ( Länder ) as well as the Municipalities ( Kommunen ). Many direct and indirect taxes exist, whereof income tax and VAT are the most relevant. The German… … Wikipedia
Мой метод анализа акций
До того как вложить деньги в акцию я люблю ее хорошенько копнуть. Но прежде чем углубиться в раскопки, я решаю, стоит ли начинать копать. Для этого захожу на сайт Finviz.com, ввожу в поиск тикер или название компании, например, Guess’ Inc. (NYSE:GES) и на открывшейся странице прохожусь по ее профилю и показателям.
На что я смотрю прежде всего? На то, к какой отрасли и к какой стране принадлежит компания. Узнать это можно сразу под графиком (п.1 на рис.1). Как видно, Guess’ Inc. работает в сфере услуг розничной торговли и зарегистрирована в США (Services | Apparel Stores | USA, п.2 на рис.1). Данная информация помогает мне:

Рис.1. Показатели акции компании Guess’ Inc. (GES) на сайте Finviz.com
Другое дело, если акция снижалась в цене: в упавших бумагах бывает скрыт потенциал, но чтобы его распознать, нужно разобраться в причинах падения. О них можно узнать из новостей, размещенных на странице чуть ниже, и по результатам продаж (Sales Q/Q) и прибыли (EPS Q/Q) в квартальном отчете.
Если отчет вышел недавно (его дата видна в поле Earnings, п.3 на рис.1), то дело, скорей всего, именно в нем и нужно смотреть его цифры. С Finviza до данных отчета — всего один клик. Справа вверху над таблицей есть две неприметные ссылки: Financial Highlights и Statements (п.4 на рис.1). Statements дает сводку данных отчетов, а Financial Highlights сравнивает результаты отчета с ожиданиями рынка.
Как видно, у Guess’ Inc. упали продажи и прибыль, что и сказалось на курсе бумаг и на ее ценовых коэффициентах (о каждом из них я подробно пишу в GO Invest). Так как я инвестирую в недооцененные акции, то меня всегда интересует цена. Понять, насколько она высока или низка относительно рынка, мне позволяет анализ стоимостных (ценовых) коэффициентов (п.5 на рис.1). В основном я использую следующие из них:
Но прежде чем я расскажу, как их трактовать, отмечу полезную фишку Finviz — цветовые подсказки. Благодаря ей «читать» показатели значительно легче. Черный цвет означает, что коэффициент в норме; зеленый — что он лучше нормы, красный — что хуже. Наглядно и просто, как я люблю.
Ценовые коэффициенты
На коэффициент P/B я смотрю в последнюю очередь, так как он не отражает способность компании генерировать прибыль. Кроме этого, P/B применим для тех компаний, у которых есть материальные активы (производства, здания, земля), и не подходит для технологичных и сервисных компаний, где основные активы — нематериальные (ПО, патенты, торговые марки).
Финансовые коэффициенты
Для того, чтобы узнать, не перегружен ли бизнес долгами, я смотрю на коэффициент покрытия долгов собственными средствами, он же долг на собственный капитал (Debt/Eq).
Debt/Eq (Долг на собственный капитал) Коэффициент Debt/Eq (п.7 на рис.1) показывает долю заемных средств в собственном капитале, то есть принадлежащем акционерам компании. Debt/Eq = 0,5 можно считать нормой, но чем он ниже, тем лучше. Однако если компания совсем не использует заемные средства, то упускает возможность увеличить отдачу на собственный капитал и снизить налог на прибыль, получив т. н. налоговый щит.
Анализируя значение Debt/Eq, я соотношу его с коэффициентом LT Debt/Eq (п.7 на рис.1). В отличие от Debt/Eq, учитывающего все долги (и краткосрочные, и долгосрочные), LT Debt/Eq отражает только долю длинных долгов. Хорошо, когда долги компании долгосрочные, так она менее уязвима со стороны кредиторов. Но здесь важно учитывать ситуацию на рынке с процентными ставками и вероятность их изменения.
Коэффициенты ликвидности
Для оценки платежеспособности компании я смотрю на коэффициенты ее ликвидности (п.8 на рис.1): они дают мне ответ на вопрос, достаточно ли у бизнеса средств для поддержания своей работы и насколько легко он способен платить по своим обязательствам.
Наиболее консервативную оценку дает коэффициент срочной ликвидности (Quick Ratio), потому как учитывает быстро реализуемые активы (деньги, вложения, дебиторскую задолженность). Quick Ratio ≥ 1 является нормой. При меньшем значении у компании может возникнуть дефицит средств для ведения текущей деятельности.
В отличие от Quick Ratio показатель текущей ликвидности (Current Ratio) учитывает более трудно реализуемые складские запасы. Current Ratio ≥ 2 считается нормой. Current Ratio ★39
Underlying Profit
What is Underlying Profit?
Underlying profit is a calculation made internally by a company to show what it believes is a more accurate reflection of how much money it generates. The number focuses on regular accounting cycle events and often excludes one-time charges or infrequent occurrences. Underlying profit differs from the required accounting profit that is recorded on financial statements and other mandatory documents that follow preset practices, rules, and regulations.
Key Takeaways
How Underlying Profit Works
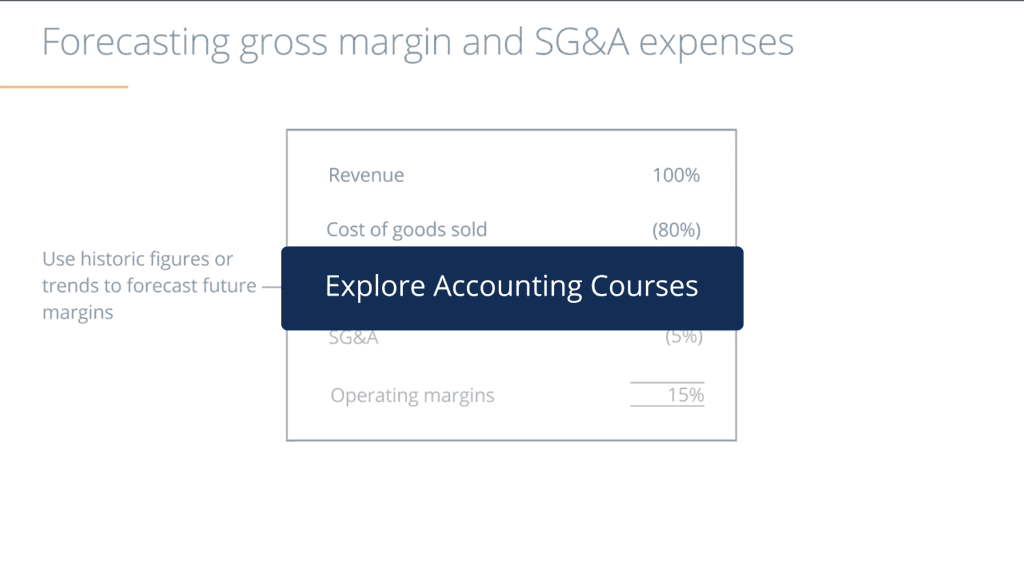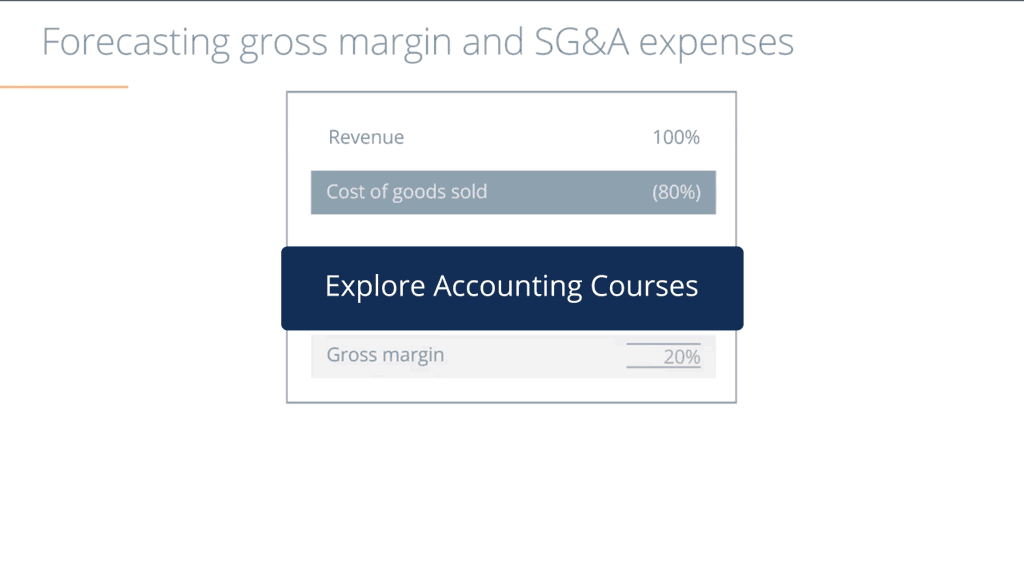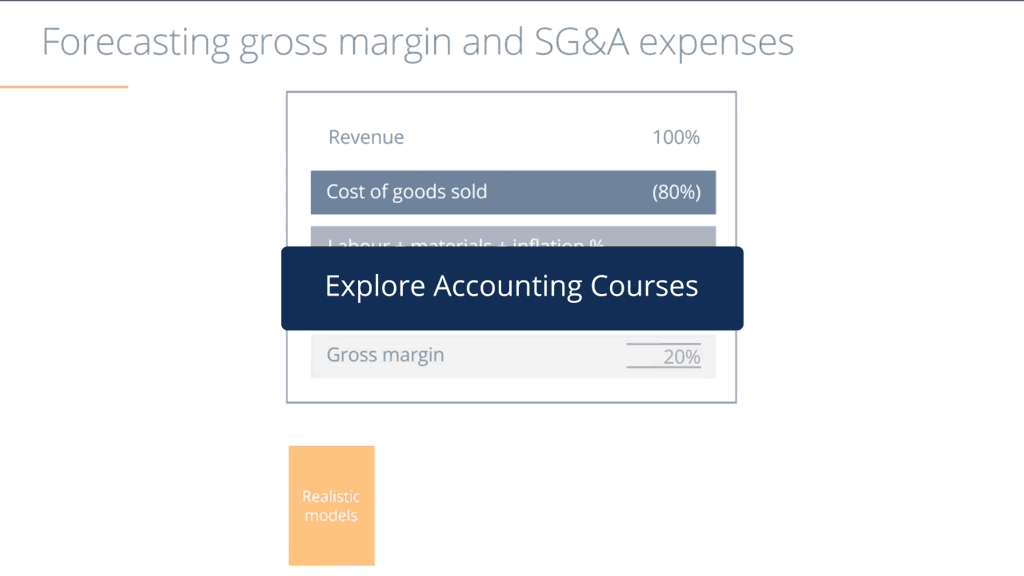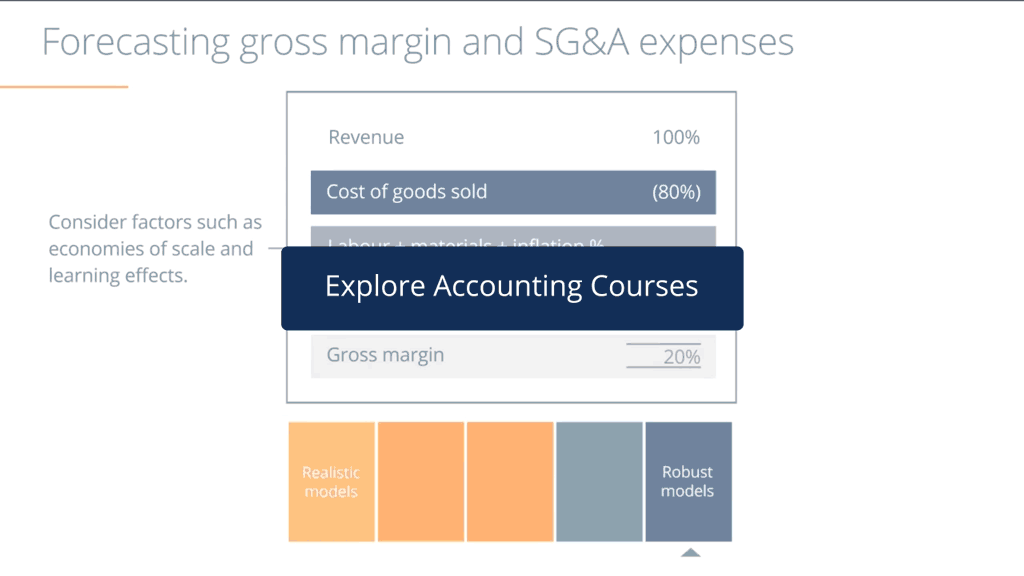
When companies publish their financials, generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require them to disclose how much profit they generated. This is calculated by subtracting all dollar costs from revenue, the same calculation used to determine how much income tax to pay.
Often, companies will choose to supplement this figure with their own calculation. Underlying profit is designed to offer a more useful indicator of performance on a year-by-year basis.
Stripping out unusual, non-recurring costs, such as natural disaster damage charges, irons out random fluctuations and should, in theory, make it easier for investors to get a better idea of how the company’s profit from its everyday, standard business operations varies over several fiscal years.
Important
Companies often use underlying profit figures for business planning purposes.
The goal here is to eliminate any distractions caused by random occurrences. Losses or gains that do not regularly crop up, such as restructuring charges or the buying or selling of land or property, are usually not taken into account because they do not occur often and, as a result, are not deemed to reflect the everyday costs of running the business.
In general, only regular operating expenses considered to be predictable or required will be deducted from gross sales in order to arrive at the underlying profit. They can include the following:
Example of a One-Time Event Removed for the Calculation of Underlying Profit
If a company is in full ownership of two buildings, and one is currently in use while one is sitting vacant, it may choose to sell the vacant building. While the sale of this asset must be recorded for standard accounting purposes, it is excluded from the calculation of underlying profit.
The sale of a large asset, such as a building, is not a standard part of the business’s operation and is not expected to occur again soon. Though it has resulted in a form of income, it is not likely to be repeated in subsequent accounting cycles for the company.
Advantages of Underlying Profit
Aside from giving investors an indication of how much money a company makes from its standard business operations, underlying profit is also used by management for business planning.
A business plan is a functional road map providing direction as to how the company will operate and is often the founding document drafted by new ventures. From an accounting perspective, the business plan also denotes the expected expenses that must be covered over a particular period of time.
When determining what operating costs can be reasonably covered, a business may prefer to remove any one-time or highly irregular financial transactions that may falsely inflate profit norms. This creates a plan based on more common occurrences that can be anticipated.
Disadvantages of Underlying Profit
Each company has its own version of underlying profit, taking the accounting profit and then making adjustments as it sees fit. Without clear guidelines on how to report underlying profit, these figures cannot be relied on to compare different firms.
Full freedom also means some of these calculations can be called into question. On occasions, firms exclude items that have a negative impact on GAAP earnings over several quarters and then promote their underlying profit figure actively as if it is the only number that merits attention.
It is important for investors to recognize the difference between accounting profit and underlying profit and gain a solid understanding of how the latter was calculated — companies will disclose this information in their financial statements.
Using the underlying profit figure can come in handy, alongside other financials, when assessing whether to invest in a company. That said, approach with caution and be sure to determine exactly why certain expenses were ignored before taking the figure at face value.
Underlying Profit
What is Underlying Profit?
Underlying profit is an internal profit calculation that a company uses as it more accurately portrays the earnings of the business than a standard accounting metric such as net profit.
Canadian companies typically follow the IFRS IFRS Standards IFRS standards are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) that consist of a set of accounting rules that determine how transactions and other accounting events are required to be reported in financial statements. They are designed to maintain credibility and transparency in the financial world ; however, financial regulatory agencies in Canada provide an exception for Canadian companies that are required to report their financial statements in the U.S.
Summary
The Underlying Profit Metric – Calculation and Example
So, what exactly is “underlying profit,” and how does it differ from the traditional earnings or the net income figure? Why do some companies think that it’s a more accurate representation of their actual profitability? The answer, of course, lies in what comprises the calculation of underlying profit.
The calculation of underlying profit – as opposed to what is referred to as “statutory profit,” the profit figure that is required to be reported in a company’s annual income statement Income Statement The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. The profit or – typically excludes certain figures that are included in the calculation of the statutory profit number. For example, a calculation of underlying profit often excludes what are known as “one-off” gains or losses for a company.
Assume that a company decides to sell off one of its major assets – a manufacturing plant – because company executives believe the business can operate more efficiently by consolidating all of its manufacturing processes at its main manufacturing facility. The sale of such a major asset might produce an extraordinarily large gain, which is added to net income.
Therefore, the company might well choose to calculate the underlying profit figure that excludes the one-time profit from the sale of its manufacturing facility, because that would be more representative of the company’s ordinary earnings from its core business operations.
The example above illustrates the fact that underlying profit calculations look to exclude unusual income or expenses the company experiences as a result of events that are not likely to recur year-to-year in the company’s regular course of doing business.
As another example, an underlying profit figure may also exclude anything that the company considers an extraordinary, non-recurring expense, such as a substantial payout of severance pay that might occur when a company decides to significantly reduce its workforce.
Financial analysts often exclude anything considered a one-time charge when they create a financial model with the purpose of projecting the future earnings of a business.
Sometimes, an entire industry may gradually shift what it considers to be the calculation that most accurately reflects its true earnings. For example, the pharmaceutical industry as a whole has, over time, come to the decision that research and development impairments should not be included in regular earnings calculation, and, therefore, pharmaceutical companies regularly exclude that cost when calculating underlying profit.
Extra profits or losses that are the result of foreign currency exchange rate changes are another common exclusion from calculating underlying profit. While such profits or losses are real, they (a) are not a result of the company’s ordinary business actions, and (b) will change from year to year, and a company has no control over whether the changes will be favorable or unfavorable for its bottom line.
A Cautionary Note
An underlying profit figure may indeed be helpful to investors and analysts by providing them with a more reliable representation of how a company is doing in terms of generating profits from year to year. However, it’s also possible that an underlying profit that a company refers to muddies up rather than clarifies things.
Some companies have been found to publish an underlying profit figure that appears favorable, but that, in fact, represents an attempt to hide the company’s real expenses and make it appear more profitable than it actually is.
Financial analysts should, therefore, always exercise great care when constructing a financial model so that what’s included and excluded results in the most accurate projection possible of the likely future earnings of a business.
Whether the figure is accurate or inaccurate, investors should pay attention whenever a company presents an underlying profit figure that differs significantly from its reported statutory profit.
Related Topics
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI’s Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. The following related CFI resources will be helpful in furthering your financial education and advancing your career:
Free Accounting Courses
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes.
These courses will give the confidence you need to perform world-class financial analyst work. Start now!
Building confidence in your accounting skills is easy with CFI courses! Enroll now for FREE to start advancing your career!
Underlying profit что такое
Что такое андерлаинг (underlying)?
Спасибо, Ваш голос учтён
Что такое андерлаинг (underlying)?
Андерлаинг (underlying) относится как к акциям, так и к производным инструментам. В деривативах под андерлаинг понимается обеспечение, которое должно быть предоставлено при исполнении производного контракта, такого как опцион пут или колл.
Спасибо, Ваш голос учтён
Комментарий
1) Деривативы. Это контракт между сторонами, основывающийся на будущей стоимости базисного актива. В текущем контексте андерлаингом будет являться актив, который должен быть поставлен, когда деривативный контракт, чем может быть пулл или колл опцион.
2) В контексте личного капитала андерлаингом называют акции, которые необходимо поставить либо когда осуществляется варрант, или право покупать акции по цене ниже рыночной, либо когда привилегированная акция или облигация преобразовывается в простую акцию.
Так как цена андерлаинга определяет цену производных ценных бумаг, то и при изменении его цены тут же изменяется цена производного актива, связанного с андерлаингом. Итак андерлаинг это ценная бумага, будь то акция или товар.
Спасибо, Ваш голос учтён
Комментарий
Что такое андерлаинг (underlying)?
Что стоит знать? Всегда нужно смотреть не на цену дериватива, а на базовой актив. Если меняется цена на золото, то автоматически меняется и цена на фьючерс, в основе которого лежит золото.
Спасибо, Ваш голос учтён
Комментарий
Что такое андерлаинг (underlying)?
Зачастую, при заимствовании из иностранного языка, может становится непонятным смысл различных слов. Слово «андерлаинг» как раз из этой оперы. Если переводить английское «underlying«, то по-русски это будет «лежащий в основе«, собственно в этом и кроется весь смысл.
Если мы возьмем контракт с поставкой актива в будущей, например фьючерс на нефть Brent, то в основе такого контракта лежит сам товар, то есть баррель нефти марки Brent. В данном случае именно лежащий в основе товар и будет являться андерлаингом.
Такая же ситуация и с отсрочкой поставки акций по опционному контракту или при конвертации облигаций в акции. В будущем, при исполнении контракта, акции должны быть поставлены, а значит они лежат в основе контракта и являются его андерлаингом.
Интересно, что с развитием данных рынков появились расчетные инструменты, которые по сути не подразумевают поставку товара, а являются чистой спекуляцией на его цене, но в любом случае в основе таких инструментов тоже будет лежать цена на конкретный актив, а значит и сам актив будет являться андерлаингом.
Понятное дело, что именно от цены андерлаинга (актива лежащего в основе) и будет зависеть цена производных контрактов, то есть если цена на нефть будет расти, то и фьючерс тоже будет показывать рост, поскольку именно на нефти он и базируется.
Спасибо, Ваш голос учтён
Комментарий
Под андерлаингом понимается ценная бумага или актив, из которого производный инструмент (например, фьючерсы, опционы) извлекает свою стоимость. По сути, это акции, облигации, валюта, товар, индекс или процентная ставка, используемые в качестве основы производного контракта.
Хотя существует множество как распространенных, так и редких деривативов, все они основаны на андерлаинге. Цена производного инструмента будет изменена, когда цена андерлаинга будет двигаться вверх или вниз. Трейдеру важно провести анализ андерлаинга, чтобы застраховаться от риска и использовать опцион и лежащую в его основе безопасность в своих интересах. После чего закрытые позиции становятся менее рискованными, потому что трейдер уже владеет андерлаингом по известной цене. Если ему придется исполнять опцион, например, продавая акции при исполнении опциона «колл», его позиция будет иметь меньший риск, так как в его активе числится базовый андерлаинг.
Как следствие, инвесторы и трейдеры часто используют концепцию базового андерлаинга в торговле опционами по двум основным причинам: для спекуляций и для хеджирования риска. Когда трейдер покупает опционы, чтобы спекулировать на будущих движениях цен на акции, тем самым он ограничивает свой риск снижения, но, в свою очередь, потенциал роста прибыли становится неограниченным.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/daniel_liberto-5bfc2715c9e77c0051432901.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JBJHeadshot-JanetBerry-Johnson-238498f91a144bf082ed759d0b1c86a8.jpg)